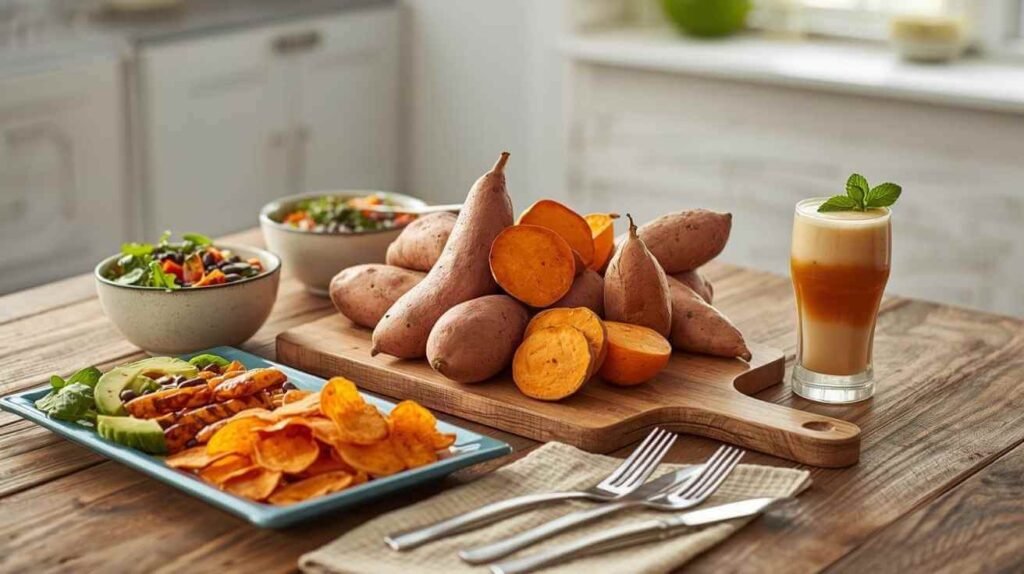
Sweet potatoes are no longer confined to holiday casseroles or traditional side dishes. Nutrition experts say this vibrant root vegetable is increasingly recognized as a functional food — delivering measurable health benefits while adapting to modern diets and wellness trends across the United States.
From smoothies to baked goods and even plant-based protein bowls, sweet potatoes are showing up in innovative ways. Dietitians point to their nutrient density, fiber content, and natural sweetness as key reasons for their expanding popularity in 2026.
A Nutritional Profile That Stands Out
Sweet potatoes are rich in beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A — essential for immune health, skin integrity, and vision. They also provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, potassium, and antioxidants.
Unlike refined carbohydrate sources, sweet potatoes release energy gradually, helping stabilize blood sugar levels when consumed in balanced portions.
Why Dietitians Call It “Functional”
Functional foods are those that offer health benefits beyond basic nutrition. According to registered dietitians, sweet potatoes support:
- Digestive health through fiber content
- Immune system support via vitamin A
- Heart health with potassium
- Anti-inflammatory benefits from antioxidants
Experts note that preparation methods matter. Baking, roasting, or steaming preserves most of the nutrient profile, while excessive added sugars or deep frying may reduce overall health value.
Expanding Beyond Traditional Meals
Food trend analysts say sweet potatoes are increasingly used in:
- Breakfast hash bowls
- Smoothies for natural sweetness
- Gluten-free baking alternatives
- Plant-based meal prep
- Sports nutrition meals
Athletes and active individuals favor sweet potatoes for their carbohydrate quality and sustained energy release.
Sweet Potato Nutrition Snapshot (Per 1 Medium Baked Sweet Potato)
| Nutrient | Approximate Amount | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | ~100–115 | Energy source |
| Fiber | ~4 grams | Digestive support |
| Vitamin A | Over 100% Daily Value | Immune & eye health |
| Potassium | ~400 mg | Muscle & heart function |
| Vitamin C | ~20% Daily Value | Antioxidant support |
A Sustainable Crop Choice
Agricultural experts highlight that sweet potatoes are relatively resilient crops. They grow efficiently in various climates and require fewer inputs than some other carbohydrate staples, contributing to their rising demand in domestic markets.
Health Considerations
While nutritious, sweet potatoes should be consumed as part of a balanced diet. Individuals managing blood sugar levels should pair them with protein and healthy fats to moderate glycemic response.

Outlook
As consumer interest in nutrient-dense, whole foods continues to rise in 2026, sweet potatoes are positioned to remain a versatile staple in American kitchens. Nutrition professionals predict continued innovation in prepared foods, plant-based recipes, and performance-focused meal plans centered around this adaptable root vegetable.
Beyond tradition, the sweet potato is emerging as a functional ingredient aligned with modern health priorities — combining flavor, flexibility, and measurable nutritional value.