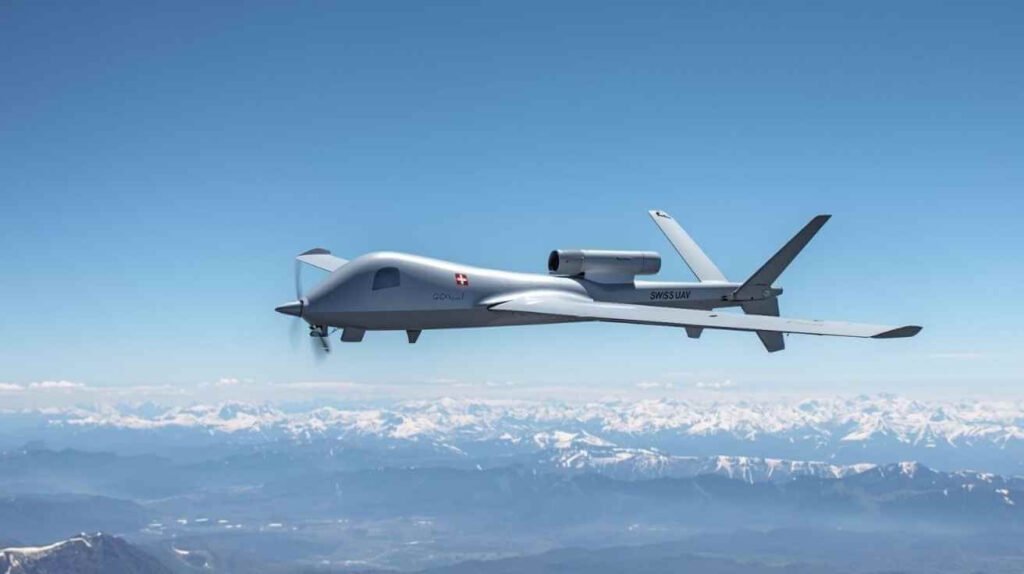
France’s defence industry is drawing renewed attention to EyePulse, a next-generation unmanned aerial system developed by Daher, as military analysts question why the platform has yet to secure widespread adoption within national armed forces. Positioned as a lightweight, high-endurance drone designed for surveillance and tactical missions, EyePulse is increasingly viewed as a potentially valuable asset in an era defined by drone-centric warfare.
Industry observers say the aircraft represents both technological promise and a missed opportunity amid rapidly evolving defence requirements.
Designed for Modern Tactical Operations
EyePulse was engineered to address the growing need for flexible, long-endurance reconnaissance drones capable of operating in contested environments. According to company briefings, the system emphasizes efficiency, low operational costs, and compatibility with intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) roles.
Defence specialists note that such capabilities are increasingly critical as modern conflicts highlight the importance of persistent aerial monitoring and rapid situational awareness.
Why Has Adoption Been Limited?
Despite positive technical evaluations, EyePulse has not yet become a core component of French military drone fleets. Analysts cite several possible explanations, including procurement prioritization, budget constraints, integration timelines, and competition from alternative unmanned platforms.
Military acquisition experts emphasize that even promising systems can face lengthy approval cycles and operational validation requirements before entering service.

Strategic Relevance in the Drone Era
Recent conflicts have underscored the expanding role of drones in surveillance, targeting, and electronic warfare support. Platforms offering extended endurance and rapid deployment are viewed as especially valuable for both conventional and hybrid warfare scenarios.
EyePulse’s design philosophy aligns with growing demand for drones that bridge the gap between small tactical quadcopters and larger, more complex UAV systems.
Industrial and Economic Implications
For Daher, broader adoption of EyePulse could strengthen France’s domestic drone ecosystem, supporting industrial competitiveness and technological sovereignty. Defence economists say investment in national unmanned systems helps reduce reliance on foreign suppliers while fostering innovation across aerospace and electronics sectors.
Regional manufacturing and engineering employment could also benefit from scaled production.
Challenges Facing Future Deployment
Experts caution that success will depend on meeting evolving operational demands, including resilience against electronic jamming, secure communications, and seamless integration with existing command-and-control networks.
Interoperability with allied systems and compliance with defence certification standards remain key hurdles.
Outlook
While EyePulse has yet to secure major domestic deployment, defence analysts argue that its prospects remain strong as military doctrine increasingly prioritizes unmanned capabilities. Procurement strategies can shift rapidly in response to emerging threats and technological advances.
For now, EyePulse stands as a symbol of both innovation and debate — a drone many believe could play a meaningful role in France’s future defence posture if strategic and operational alignment materializes.