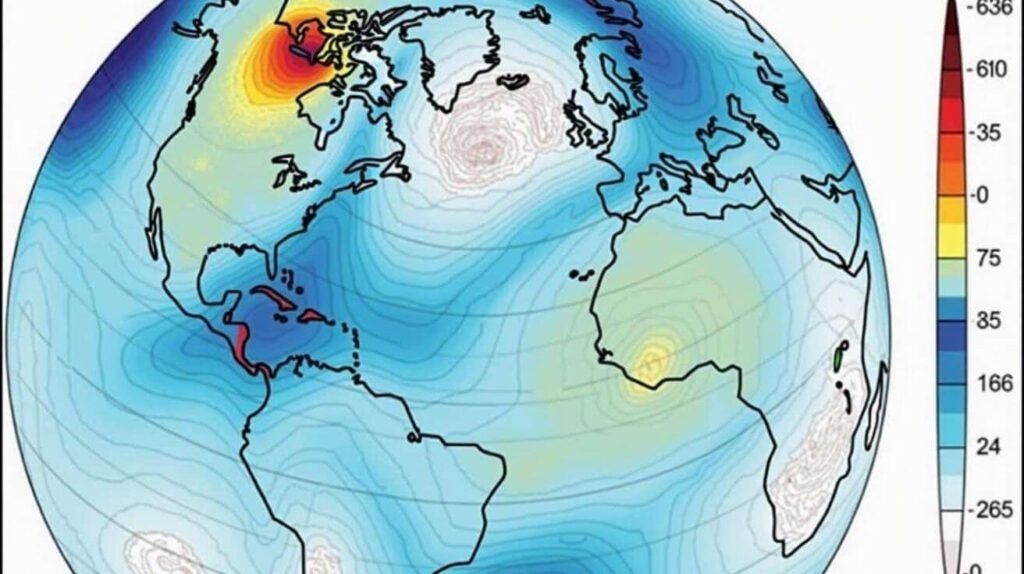
Meteorologists are warning of an unprecedented polar vortex anomaly barreling toward North America and Europe. Analysts say its speed, trajectory, and structural intensity are unlike anything recorded in decades, raising the prospect of extreme winter conditions across multiple regions.
The anomaly is centered over the Arctic Circle but is expected to push southward into populated areas of the United States, Canada, and parts of the United Kingdom in the coming days.
What Makes This Polar Vortex Different
Forecasters note several unusual features that distinguish this event from typical winter storms:
| Factor | Observation | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Rapid southward movement | Shorter warning times for affected regions |
| Structure | Deep, tightly circulating core | More severe wind chill and sustained cold |
| Temperature Gradient | Extreme difference between Arctic and mid-latitudes | Amplified storm development |
| Duration | Expected persistence for 5–7 days | Prolonged snow, ice, and subzero conditions |
The rapid displacement of Arctic air masses is forcing meteorologists to update models hourly, as traditional winter patterns appear increasingly unreliable.

Expected Regional Effects
- United States: Midwestern and Northeastern states may experience record low temperatures, heavy snowfall, and infrastructure strain.
- Canada: Prairie provinces and Ontario face extreme wind chill and potential power outages.
- United Kingdom: Sudden cold snaps could disrupt transport and heating systems, with rare snowfalls in southern regions.
Authorities in all affected regions are urging residents to prepare for sudden temperature drops and hazardous travel conditions.
Climate Context
Climate scientists caution that polar vortex anomalies are becoming more frequent and intense, linked to Arctic warming and jet stream disruptions. Such events are increasingly testing the resilience of urban centers, transportation networks, and energy infrastructure.
The Bigger Picture
This approaching polar vortex anomaly is a reminder of the complex interplay between Arctic climate shifts and mid-latitude weather extremes. As winter 2026 unfolds, policymakers and residents alike face the urgent task of adapting to volatile, record-breaking weather patterns that could redefine what “normal” winter conditions look like.